Located at 20 Old Brompton Road – Just Steps from ![]() South Kensington Tube. Easy Access, Always.
South Kensington Tube. Easy Access, Always.
Private Smear Test (PAP Test ) in London
Cervical smear test – commonly referred to as a smear or PAP smear – is an essential screening tool for checking early indications of cervical cancer and diagnosing the occurrence of HPV (human papillomavirus). At Gynae UK Clinic, we provide rapid and convenient private smear tests in London with a private GP who is specialist in gynaecology. Regular cervical screening is a crucial method to check your cervix’s health.
We test for HPV through our screening. If HPV is detected, we then look for abnormal cells that may result in cervical cancer. The sooner these cells are found, the less chance there is of cancer formation. If you are tested positive for HPV, we can also offer HPV sub-typing to find out if the type is high-risk or low-risk.
We offer the HPV vaccine, ideally before becoming sexually active. If you are already sexually active, HPV vaccination may still provide protection against strains you have not been exposed to. We recommend checking your current HPV status first. If your results show anything abnormal, we can refer you to a self-pay private specialist or refer you to an GP to have further tests done and be treated.
For further details or to schedule an appointment with our healthcare specialist, simply contact us on 020 7183 5411.
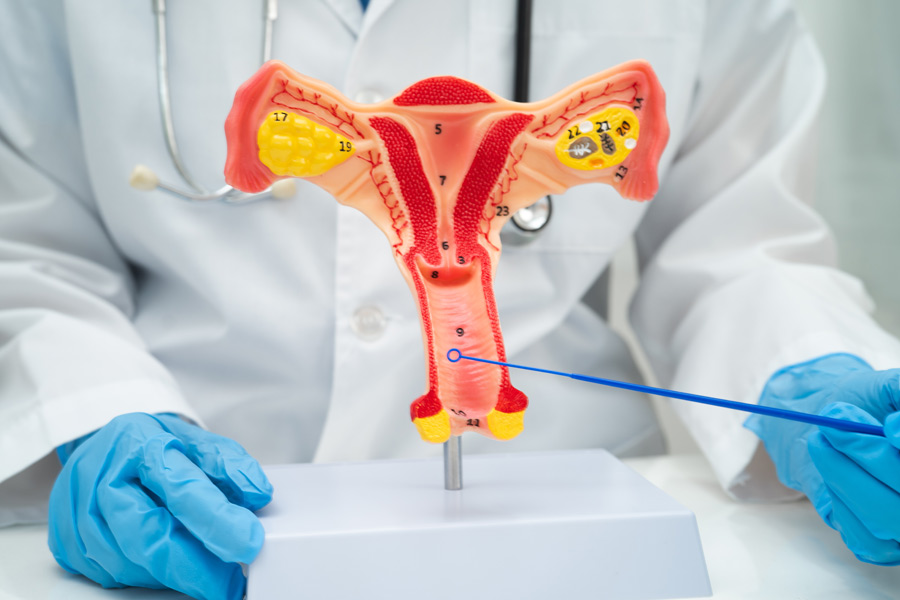
What is a cervical smear test?
A cervical smear test is performed to identify if there are any abnormalities in the cells of your cervix. It is also referred to as a PAP test or PAP smear test, and these names are used interchangeably. The test will confirm any kind of uncertainties in your cervical cells. These abnormalities may turn into cancer cells in the long run. When you discover abnormal signs in the cells, it is crucial to treat them once the PAP test is done.
Why opt for a Private Smear Test?
Private smear tests enable early diagnosis of abnormal changes, which can be life-saving. Advantages of opting for Gynae UK in London include:
- Personalised experiences from our dedicated staff
- Options to test beyond age guidelines
- No referral from a GP is needed
- Instant access to colposcopy if high-risk HPV is identified
Prior to the Treatment
You will get to have a formal consultation with a healthcare professional. At this point you will be in a position to discuss your detailed medical history, symptoms, concerns and ask any questions that you may have.
We will also talk to you about whether you need any additional diagnostic tests, like blood tests or scans. Any additional charges will be explained before performing the further tests.
BOOK ONLINE NOWHow to Prepare for a Private Smear Test?
Plan the timing
Try to have the test in the middle of your menstrual cycle, meaning not during your periods.
Cut down on some activities
Stay away from any type of sexual intercourse, lubricants, tampons or vaginal medications for at least 24 hours from before the test.
Wear comfortable clothing
Dress in something easy to remove from your waist down.
Relaxation
Get relaxed and have a painkiller if you are likely to feel uncomfortable.
Being Aware of the Procedure
It is important to know beforehand that the test entails a speculum and a brush for collecting cells.
Aftercare Following the Test
Minor discomfort or spotting are likely to occur, and you may return to normal activities immediately.
Wait for Results
Usually, it will require 3 to 5 working days before getting results.
Go for Regular Screening
Adhere to your doctor’s recommendations regarding screening frequency.
Receiving Your Smear Tests Results
You can usually get the smear test results in a period of 3 to 5 working days and they will be sent securely to you, typically by email. Out of every 10 smear test results, 9 come out normal, which means it is not much concerning. If your test results are normal, you only need to keep getting routine tests in every 3 years.
Inadequate Results
Sometimes the outcomes of smear tests can also turn out to be insufficient and this is the case when the sample has been made up of a minimal group of cell. It may also be the case when the cells could not have been seen distinctly. This is usually the source of infection which implies that you will need to redo the test in 3 more months.
Abnormal Results
Abnormal results do not necessarily indicate cervical cancer. They mean there are changes to the cells in your cervix. This is sometimes called dyskaryosis and in many cases, these changes may resolve naturally. But in some women, these changes will develop into cervical cancer if not treated timely. The result varies depending on the degree of abnormality of your cells.
Borderline or Mild Results
Borderline or mild changes suggest that we will conduct a second test which is going to check for HPV or high-risk human papillomavirus. If we find any evidence of the HPV virus, we will recommend you for a test named colposcopy in order to take a better look at your cervix. If no traces of high-risk HPV are found in the test, then you have only a low probability of getting cervical cancer. This implies that you can just keep performing routine smear tests.
Moderate or Severe Results
Moderate to severe changes indicate that your cervical cells will not recover on their own. This means you will be asked to attend colposcopy so that your cervix can be investigated with more detail. This will help us determine what treatment you may require.

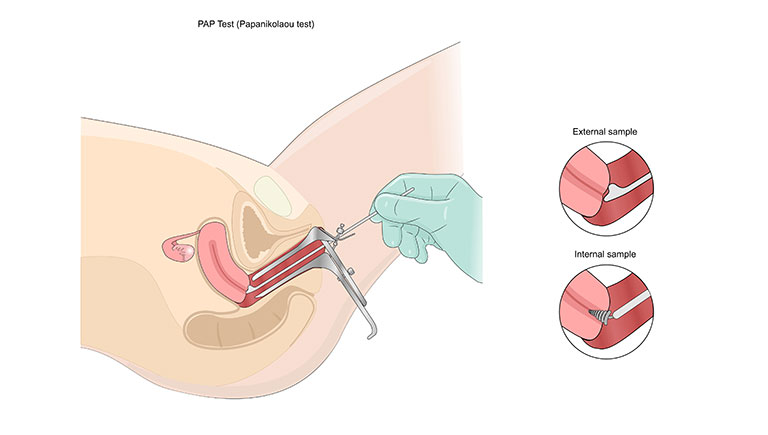
The Procedure
While you are undergoing a smear test, our healthcare provider inserts a metal or plastic object called speculum carefully into the vagina to expose the cervix (the womb’s neck). Next a small soft brush is used to take a sample of cells from the cervix. The test is quite comfortable as reported by most women.
The cell samples are left in a plastic container filled with fluid for examination under the microscope. This technique has drastically brought down the rates of inadequate smears. Only 1 in every 20 smears requires repeat testing as per recent reports. Results are usually available within 3 to 5 working days, and most tests return normal findings.
One out of every 20 women can detect abnormal cells through a smear test. If the result of a smear test is borderline or mildly abnormal, then the laboratory carries out the HPV test. This will decide whether further testing is necessary.
Aftercare
Your results will typically be available within 3 to 5 working days. We will send them to you securely, and if any abnormalities are detected, we will contact you promptly to discuss the next steps and arrange follow-up care. For confidentiality reasons, results are not provided over the phone.
Is a Private Smear Test expensive?
Our private Cervical Smear Test costs from £190 and includes histology and HPV testing.
Why have a Private Smear Test with us at Gynae UK Clinic?
Here at Gynae UK Clinic, we provide a number of women’s health services such as private smear tests and HPV tests. We know that you might feel nervous when undergoing a smear test, particularly if you have never had one before. Our nurses and doctors at our private GP clinic are here to make you feel relaxed and comfortable during the entire testing experience. You can receive the results within 3 to 5 working days so you are never left in suspense.
You are able to book your individual smear test and HPV test at any time on our online booking system or by phone. Gynae UK provides same day smear test and cervical screening appointments as well as other women’s health services.
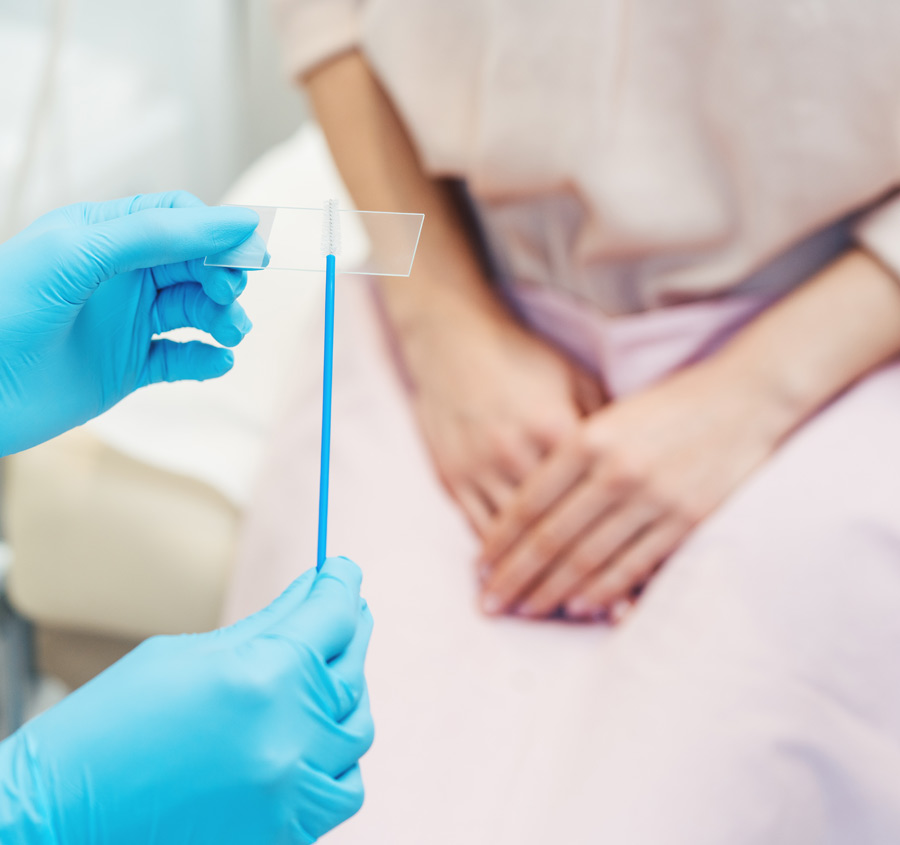
What can I expect from my Smear Test?
- You are able to choose whether you would prefer a chaperone present in the room with you during the appointment.
- You will be required to undress from the waist downwards. This is usually done behind a screen or in another secluded region. When ready, you will be allowed to cover yourself with a sheet given to you.
- The doctor or nurse will request you to lie on your back, generally with your legs bent, feet together and knees apart.
- Next the doctor or the nurse will gently insert a smooth, tube-shaped instrument called speculum into your vagina.
- Then they will open the speculum to take a closer look at your cervix – this does not usually hurt, but might be uncomfortable for a while.
- You can request your provider to stop the procedure any moment.
- Next they will collect a small cell sample from your cervix with the help of a soft brush.
- The doctor or nurse will then close the speculum, remove it from your vagina, and let you dress.
- The cell sample will then be sent out for examination.
GYNAE UK Clinic has a variety of women’s health packages that include several tests and check-ups. Private cervical screenings are included in many of these packages, but smear tests can be provided separately as well.
FAQs
What is a smear test?
A smear test, or cervical screening, is a preventive healthcare assessment carried out to identify abnormal cells in the cervix before they have the opportunity to progress into cervical cancer. The test consists of taking a small sample of cells from the cervix with a soft brush and having them analysed at a laboratory.
This fast and easy process is an important aspect of women’s health in the UK. It is advised for women aged between 25 and 64, as screening at regular intervals can greatly lower the risks of cervical cancer by diagnosing and treating abnormalities before they turn malignant.
What is HPV?
Human Papillomavirus (HPV) is a type of viral infection that affects the body cavity linings as well as the skin. The infection has no symptoms mostly and is spread through contact between skin.
How common is HPV?
8 out of every 10 individuals tend to get infected with HPV at some stage of their lifetime in the UK. HPV is highly prevalent and spreads mainly through intimate skin-to-skin contact, including genital, oral, and anal contact. There are numerous varieties of HPV of which most are benign, but some 30 of them lead to cancer (cervical cancer).
What do I do after getting the test?
Regular smear tests are an important aspect of women’s health and getting it privately has several advantages:
- You can arrange your appointment with our GPs at a time that is convenient to you
- Your test results are returned within 3 to 5 working days from when you were tested
- We provide an added screening for Human Papilloma Virus (HPV)
- We are able to arrange an urgent gynaecological referral if you require it
Is a smear test suitable for my age?
All women aged over 25 will be invited for a smear test every 3 years until they are 49, and women between the ages of 50 and 64 should get tested in every 5 years.
HPV can also be transmitted through close genital contact without penetrative sex.; so, it is necessary to book an appointment.
How to prepare for a smear test?
It is best to arrange your smear test mid-cycle, which means from 7 days after the end of your period. The test can be done at any time of the month, except during your period.
We advise you not to use lubricants, spermacides, ointments or pessaries for a couple of days prior to getting the test.
What to expect during a smear test?
A smear test takes approximately 5 minutes. A speculum is passed into your vagina to hold it open gently. A doctor or nurse will use a small brush to obtain a sample of some of the cells on your cervix. The sample is then sent to a laboratory for further analysis under a microscope.
For women aged 25 and over, we perform dual testing: screening for high-risk HPV subtypes and checking for abnormal cells via liquid-based cytology.
Is a smear test painful?
A smear test should not usually hurt, though you should talk to the nurse or doctor if you do feel pain.
You may feel a bit uncomfortable and so you should try to take nice deep breaths and keep your legs apart – this will help to relax your pelvic floor.
Should I have a smear test during my period?
It is usually advised to avoid having a smear test while you are on your period, as menstrual blood can interfere with the accuracy of the results. The ideal time for getting a smear test is in the middle of your menstrual cycle, usually 10 to 14 days from after the beginning of your last period.
However if you are booked in for a test and your period occurs unexpectedly, contact your GP surgery or clinic to reschedule the appointment. But if you have issues of irregular periods or ongoing bleeding, do not delay your screening. It is best to discuss the best option for your case with your healthcare provider.
 Click To View Full Map
Click To View Full Map
Contact Info
Phone: 020 71835411
Email: info@gynaeuk.com
Address:
20 Old Brompton Road, South Kensington, London SW7 3DL
Opening Hours
| Day | Opening Hours |
|---|---|
| Monday | 9am to 6pm |
| Tuesday | 9am to 8pm |
| Wednesday | 9am to 6pm |
| Thursday | 9am to 8pm |
| Friday | 8am to 5pm |
| Saturday | 10am to 4pm |
| Sunday | Closed |

