Located at 20 Old Brompton Road – Just Steps from ![]() South Kensington Tube. Easy Access, Always.
South Kensington Tube. Easy Access, Always.
Colposcopy
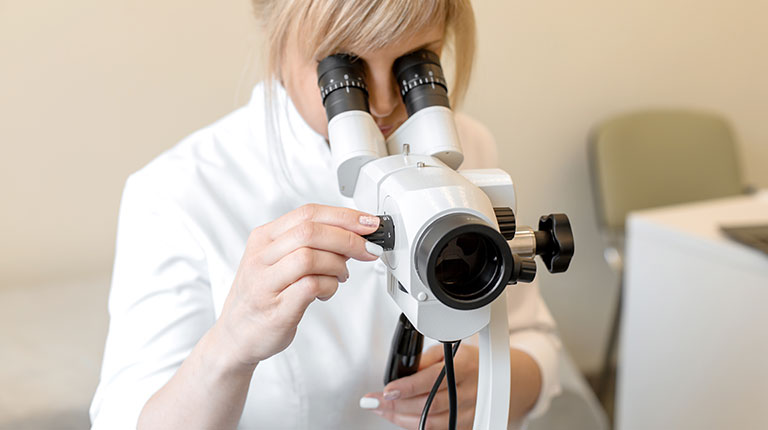
A colposcopy procedure is used to have a look at the cervix —which is the lower part of the womb located on top of the vagina.
This procedure is recommended if abnormal cells are found in your cervix during cervical screening. These cells are not usually harmful, and they typically disappear on their own.
A colposcopy can help your doctor to know whether the cells in your cervix are abnormal or not, and also helps him or her to whether you need treatment to remove them.
How to Know You Need a Colposcopy
Your doctor might refer you for a colposcopy within a few weeks of cervical screening if any of the following is observed:
- Abnormal cells in your cervix
- If after your screening test your cervix doesn’t look healthy
- Unclear test result after the different screening
A colposcopy can be used to find out the root of problems such as bleeding after sex and unusual vaginal bleeding.
You don’t have to be worried if you have been referred for a colposcopy. It is highly unlikely that you have cancer. In most cases, abnormal cells don’t get worse while you wait for your appointment.
What To Expect During A Colposcopy
A colposcopy is usually conducted in a hospital. It usually lasts for 15 - 20 minutes. Which means you may be allowed to go home the same day after the screening.
The following should be expected during the process;
- A need to undress from your waist down, but if you don’t want to undress, then you should wear a loose skirt. You will need to lie down in a particular type of chair that has full support for your legs.
- Speculum(which is a medical device) will be inserted into your vagina to open it gently
- A microscope with light will be used to look inside your cervix. Although this will not touch your cervix or enter your body.
- The nurse or doctor carrying out this procedure will apply a special liquid on your cervix — to help highlight any abnormal areas.
- Then a small sample of tissues will be removed. This is called biomass, and it will be studied in the laboratory. This process may be a bit uncomfortable for most people.
If the result shows that you have abnormal cells in your cervix, you will need treatment to remove the cells immediately. If the result is not clear, you will have to wait for your biopsy result.
Results of a Colposcopy
The result can help tell right away if you have abnormal cells in your cervix. You may have to wait for 4 - 8 weeks for your result to be ready. The result can either be normal or abnormal.
Notably, 4 out of ten women have no abnormal cells in their cervix. However, they are advised to continue going for cervical screening as usual. Also, 6 out of 10 women who have abnormal cells may require treatment to remove them.
When discussing the result of your biopsy with you, your doctor might use the term CGIN or CIN — this is merely a medical term for abnormal cells.
CIN means that there is a higher chance of the abnormal cells becoming cancerous. A high number shows that you have a high probability of cancer if the abnormal cells are not removed.
Treatment For Removing Abnormal Cells
If there is a moderate or high chance of cancer, the abnormal cells must be removed. If ignored, they can become cancerous.
Several treatment methods are used in removing the abnormal cells. These treatments are simple and effective, and they include:
- Cone Biopsy
In this method, a tissue shaped like a cone which contains the abnormal cells is cut out of your cervix. This is usually done under general anaesthetics; you will be asleep while the procedure is on-going, and you might be required to stay in the hospital for the night after the procedure.
- Large Loop Excision of The Transformation Zone
In this method, a heated wire loop is used to remove the cells. Your cervix is numbed, but the process is carried out while you are awake. Also, you can be allowed to go home on the same day as the procedure.
Next
What Happens During Colposcopy
A colposcopy is usually conducted in a hospital, and the procedure lasts for around 15 - 20 minutes plus, you can also go home after the process.
How To Prepare For A Colposcopy
You should not have sex or use a vagina medication, tampons, creams, or lubricants for at least 24 hours before this procedure.
You should come along with a sanitary pad which should be worn after the colposcopy because there may be light bleeding or discharge after the procedure. Notably, you are allowed to eat and drink, as usual; there is no diet restriction in this procedure.
You should inform the clinic if any of the following occurs before your appointment:
- Period: If you think your period will come around the time of your procedure, even though it is still possible to carry out the procedure, in some cases, you will be advised to postpone it.
- Pregnancy: If you are pregnant. The process of removing a tissue sample, also known as biopsy and any other treatment will be delayed until a few months after you have given birth, although colposcopy is safe during pregnancy.
You can come along with a family member, partner, or friend to help you feel more at ease.
The Procedures for Colposcopy
The Colposcopy process is usually carried out by an expert (a colposcopist) — this can be a nurse or doctor that is trained for this procedure. Some steps involved in this procedure include:
- You may be required to undress from your waist down. However, you are advised to wear a loose skirt, if undressing may be uncomfortable for you.
- You will lie down in a unique chair that has padded supports for your legs
- A speculum would be inserted inside into your vagina while it is gently opened. This step is similar to a cervical screening test.
- A colposcope, which is a microscope with a light, is used to look into the cervix — it stays about 12 inches (30 cm) outside your vagina, and it helps the doctor to see the cells in your cervix.
- Special liquids will be applied to your cervix — it helps highlight abnormal areas. You might feel a mild burning or tingling sensation when this liquid is used.
- A small sample tissue also referred to as biopsy, will be removed and taken for closer examination in a medical laboratory — it is not a painful procedure, but you might experience a stinging sensation or a slight pinch.
If it is inevitable that you have abnormal cells in your cervix, you will place on treatment to remove the abnormal cells immediately. If the opposite is the case, you will have to wait for your biopsy result.
What To Expect After A Colposcopy
After a colposcopy:
- You can be allowed to go home as soon as you are ready.
- You can return to your normal activities, although some women prefer to rest until the next day.
- You may have a light bleeding or a brownish vaginal discharge. This is normal and should only last for 3 - 5 days.
- You may have to wait until the bleeding stops before using a tampon or having sex. You should also avoid vaginal creams, medications, or lubricants during this period.
Your doctor or nurse will discuss further discoveries after your biopsy has been examined, and you should get your result by post in a few weeks after the test is conducted.
Women’s Health is Our Passion
Live life to the fullest with our range of Consultant-led gynaecological services.
BOOK ONLINE NOWColposcopy: The Risks And Side Effects
A colposcopy is a safe procedure that doesn’t cause any severe problems. However, some women experience:
- Pains or discomfort. If the process is so painful, you can tell the colposcopist, and they will adjust to make you more comfortable.
- You might experience brown vaginal discharge after the process. This is caused by the liquid used in highlighting the abnormal cells in your cervix — it will pass quickly.
- Light bleeding. This is caused by a biopsy, and it usually lasts for 3 - 5 days.
- If you have persistent bleeding, you should contact your nurse or doctor, and where the bleeding is more substantial than your regular flow during your period, you should also report. Stomach pain and smelly vaginal discharge should also not be taken for granted.
There are also some additional risks and side effects if you are placed on treatments to remove the abnormal cells.
Next
Results
After a colposcopy, your nurse or doctor will be able to tell you what they have observed straight away. However, if a biopsy (a small sample tissue) is taken for the examination, you will have to wait for 4 - 8 weeks to get your result.
The information below some can interpret to you what the different results mean.
- Normal Results
Studies show that about 4 in every ten women who undergo a colposcopy have a normal result. It means that no abnormal cells were present in the cervix during the colposcopy and the biopsy. They also do not need immediate treatment. However, they would be advised to continue with their usual and regular cervical screening. This is to prevent or monitor the development of abnormal cells later.
You would be invited for a cervical screening appointment in 3 - 5 years, although this depends on your age.
- Abnormal Results
It has also been observed that about 6 in every ten women have abnormal cells in their cervix. This is known as cervical intraepithelial neoplasia (CIN) or cervical Glandular intraepithelial neoplasia (CGIN) — these are not cancerous cells, but there is a risk that they can turn cancerous if they are not treated. It is possible to detect abnormal cells when colposcopy is carried out, but a biopsy would be needed to determine the type of abnormal cells and to state if it can become cancerous or whether treatment is necessary.
Below are the different types of abnormal cells and what they mean:
CIN 1: It is unlikely that these abnormal cells would become cancerous, and they can go away on their own. No treatment is needed, although you would be invited for a cervical screening test in 12 months to know if the cells have disappeared.
CIN 2: This type has a moderate chance of becoming cancerous and treatment will be recommended to remove them.
CIN 3: These cells have a high chance of becoming cancerous. And treatment is given to remove them immediately.
CGIN: There is a high chance these cells will become cancerous, and treatment is given to remove them.
In rare cases, colposcopy and biopsy can find cervical cancer. When this happens, you would be referred to an oncologist for further treatment.
Next
Treatment of Colposcopy
If a colposcopy reveals that there are abnormal cells in your cervix, immediate treatment would be needed to remove those cells. If they are left untreated, there is a high chance of them becoming cancerous. These treatments aim at removing the abnormal cells and minimising the damages to the healthy cells and tissues — it is done mostly by removing an area in the cervix. This is about the size of a fingertip.
When is Treatment Carried Out?
The treatment to remove abnormal cells can be carried out at the same time as the colposcopy. But it has to be evident that some of the cells in your cervix are abnormal.
Some treatments cannot be done on the same day — for instance; you might have to wait for your biopsy result for a few weeks if it is not clear whether you have abnormal cells in your cervix or not.
Types Of Treatments
Abnormal cells can be extracted from the cervix in many ways. Some of the procedures are listed below.
- LLETZ
This is one of the most common treatment used. It is a large loop of excision of the transformation zone (LLETZ) — in this method, abnormal cells are removed with the use of a thin wire loop heated with an electric current.
It can be conducted at the same time as the colposcopy, and it is carried out while you are conscious, although a local anaesthetic will be injected into your cervix to numb it during the treatment. Another name for LLETZ is loop diathermy, loop excision, loop biopsy, and loop cone, plus you do not have to stay overnight in the hospital.
- Cone Biopsy
This method is not as conventional as the first. It requires a minor operation to be carried out to cut out a cone-shaped piece of tissue containing the abnormal cells.
This method is used if a large area of the tissue has to be removed. It can not be carried out the same time as a colposcopy, and it is conducted under general anaesthetic, plus you might be required to stay overnight in the hospital.
Other Treatment Methods
Other ways to treat abnormal cells in the cervix are:
- Cold Coagulation: this treatment requires heat to be applied to the cervix to burn up the abnormal cells
- Laser Treatment: A laser light is used to pinpoint and destroy the abnormal cells
- Cryotherapy: In this method, the abnormal cells are frozen and destroyed. This method is used to treat minor cell changes.
- Removal of the womb (Hysterectomy): If abnormal cells have been found in your cervix more than once, and you do not wish to have more children, or you have passed the age of childbearing, and the cells are severely abnormal, this treatment method will be recommended for you.
What Happens After Treatment?
You can always return home after your treatment is finished. Most women feel healthy and active to resume their work and normal activities the following day. However, you would be advised to avoid the following:
- Driving for at least 24-hours after treatment, if a general anaesthetic was administered on you, but if a local anaesthetic was used, you could drive straight away.
- Don’t use tampons for at least four weeks — use sanitary pads instead.
- Do not have sex until after four weeks of your treatment.
- Include exercise in your daily routine, including Do these for at least two weeks or while you are still bleeding.
You will be advised to go for another cervical screening test six months after to check for any development of abnormal cells and the human papillomavirus (HPV).
If HPV is not found, you won’t be screened again for at least three years. However, if you have HPV or significant cell changes are noticed, you will be referred to go for another colposcopy.
Risks and Side Effects of Colposcopy Treatment
Common side effects of the treatments are:
- Brown vaginal discharge and light vaginal bleeding. You might also notice light vaginal discharge, and this may last for up to 4 weeks after your treatment.
- You will notice mild pain; this is similar to period pain — it should end in a few hours. You can relieve the pains by taking ibuprofen or paracetamol.
There are little risks for some severe complications such as:
- Infections: An infection can cause persistent or heavy bleeding. There can also be smelly vaginal discharge and stomach pain that is persistent. You should visit your doctor if you are experiencing this symptom.
- Premature birth: There is a slight risk of premature birth — it is more likely to occur before the 37th week of pregnancy. It is more likely in future pregnancies if you need repeated treatments or if lots of tissues have to be removed.
In most cases, the benefits of these treatments outweigh the risks. You can talk to your doctor if you have any concerns or if you need to know more about the potential dangers of this treatment.
 Click To View Full Map
Click To View Full Map
Contact Info
Phone: 020 71835411
Email: info@gynaeuk.com
Address:
20 Old Brompton Road, South Kensington, London SW7 3DL
Opening Hours
| Day | Opening Hours |
|---|---|
| Monday | 9am to 6pm |
| Tuesday | 9am to 8pm |
| Wednesday | 9am to 6pm |
| Thursday | 9am to 8pm |
| Friday | 8am to 5pm |
| Saturday | 10am to 4pm |
| Sunday | Closed |

